In today’s technology-driven world, businesses and individuals rely heavily on data.
From critical business documents to cherished memories captured in photos and videos, the value of data cannot be overstated. However, data loss is a real and constant threat, whether due to hardware failures, natural disasters, or cyberattacks.
This is where cloud backup comes to the rescue. Cloud backup is a useful tool with many benefits. However, it can also present challenges. Here, we will discuss what cloud backup is, its advantages, and the difficulties it poses. Additionally, we will provide a list of best practices to ensure a successful cloud backup strategy.
Let’s first start by discussing exactly what cloud backup is.
Cloud backup is the process of securely storing data in a remote location hosted by a service provider. It involves transmitting data over the internet to the provider’s servers, where it is encrypted and stored for safekeeping. Cloud backup ensures that data remains accessible even if the original source is compromised.
Benefits of Cloud Backup:
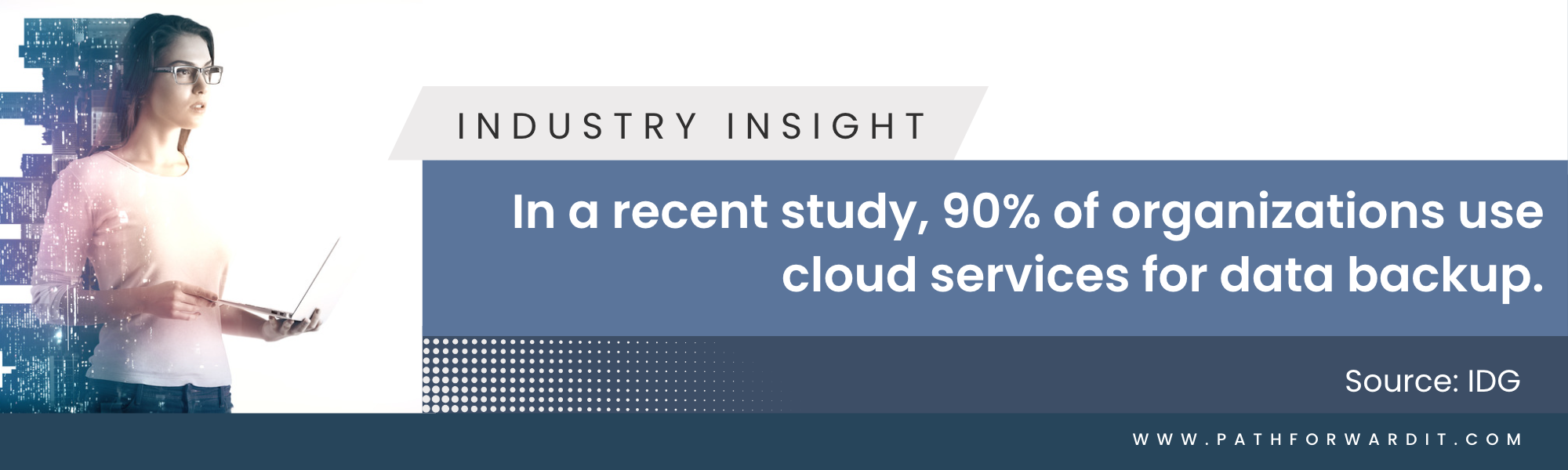
1. Data Protection and Disaster Recovery: Cloud backup offers a robust solution for safeguarding your data. By storing it off-site in multiple redundant servers, it provides protection against hardware failures, theft, natural disasters, or other catastrophic events. In a survey by IDG, it was found that 90% of organizations use cloud services for data backup, and 53% of respondents stated that their primary use case for the cloud is data backup and recovery. (Source: IDG)
2. Easy Scalability: Cloud backup services are designed to accommodate growing data needs. Whether you need to store a few gigabytes or several terabytes, you can easily scale your storage space without the hassle of purchasing and managing additional hardware.
3. Accessibility: Cloud backup enables you to access your data from anywhere as long as you have an internet connection. This accessibility is particularly beneficial for businesses with remote teams or individuals who travel frequently.
4. Cost Efficiency: Cloud backup eliminates the need for investing in expensive hardware infrastructure and maintenance costs. Service providers typically offer flexible pricing models, allowing you to pay only for the storage space you use.
5. Automated Backup: Cloud backup solutions often provide automated backup processes, reducing the risk of human error. This ensures that data is consistently and regularly backed up without manual intervention.
Challenges of Cloud Backup:
1. Bandwidth Limitations: Uploading large amounts of data to the cloud can be time-consuming, especially if your internet connection has limited upload speeds. Initial backups may require significant time and resources, but subsequent incremental backups are generally faster.
2. Security and Privacy Concerns: While cloud backup services prioritize data security, concerns about unauthorized access, data breaches, or government surveillance may deter some individuals and organizations from embracing cloud backup. Selecting reputable providers with robust security measures and encryption protocols can alleviate these concerns.
In a survey by Barracuda Networks, 44% of respondents cited security and data privacy concerns as the primary reason for not adopting cloud backup. (Source: Barracuda Networks)
3. Dependence on Internet Connectivity: Cloud backup relies on a stable and reliable internet connection. If your connection is unreliable or experiences downtime, accessing and uploading data to the cloud may be disrupted.
4. Cost Considerations: While cloud backup can be cost-effective for many, organizations with substantial data storage needs may incur higher costs over time. It is essential to carefully evaluate pricing models, including storage tiers and data transfer fees, to ensure the chosen solution aligns with your budget.
Best Practices for Cloud Backup:
1. Define Backup Strategy: Determine what data needs to be backed up, how frequently, and the retention period. Categorize data based on importance to prioritize resources effectively.
2. Select a Reliable Provider: Research and choose a reputable cloud backup provider that aligns with your security requirements. Ensure the provider offers encryption, redundancy, and compliance with data protection regulations.
3. Encryption and Data Security: Encrypt data before transmission and choose a provider that offers encryption at rest. Implement strong access controls, two-factor authentication, and regular security audits.
4. Test and Validate Backups: Regularly perform test restores to verify the integrity and availability of your backup data. This practice ensures that your backup system is functioning correctly and that your data can be restored successfully if needed.
5. Implement Versioning and Retention Policies: Enable versioning to store multiple versions of files, allowing you to recover from accidental deletions or modifications. Establish retention policies to determine how long backups are retained based on regulatory requirements and business needs.
6. Monitor and Track Backup Activity: Set up monitoring and reporting mechanisms to track backup activities, including successful backups, failures, and completion times. Regularly review logs and alerts to identify and address any issues promptly.
7. Maintain Off-Site Copies: While cloud backup provides off-site storage, it’s prudent to maintain additional copies of critical data in alternative physical locations or with a secondary backup provider. This redundancy mitigates the risk of data loss in case of a catastrophic event.
8. Regularly Update and Test Recovery Procedures: Backup alone is not enough; ensure your recovery processes are up to date and well-documented. Regularly test your recovery procedures to validate their effectiveness and identify any potential gaps or weaknesses.
9. Educate and Train Users: Promote data backup awareness and provide training to users about the importance of backing up their data. Encourage good data hygiene practices, such as saving files in designated backup folders, to ensure comprehensive data protection.
10. Review and Update Backup Strategy: Regularly evaluate and update your backup strategy to accommodate changing data requirements, business growth, and emerging technologies. Stay informed about advancements in cloud backup solutions to take advantage of new features and improvements.
Cloud backup offers a reliable and efficient way to protect your valuable data from various risks and ensure its availability in the face of unforeseen events. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and best practices associated with cloud backup, individuals and businesses can implement a robust backup strategy that safeguards their data and provides peace of mind.




